In the rapidly evolving landscape of business technology, the debate over cloud versus on-premise CRM solutions continues to gain traction. Both options offer distinct advantages and drawbacks, making the choice a critical one for organizations of all sizes.
Cloud CRM solutions promise scalability, accessibility, and lower upfront costs, while on-premise systems provide greater control, security, and customization options. As companies strive to optimize their customer relationship management strategies, understanding the nuances of each approach is essential.
This article delves into the key factors to consider when deciding which CRM solution best aligns with your business goals and operational needs.
Cloud vs. On-Premise CRM: Which One is Better?
When it comes to choosing between Cloud CRM and On-Premise CRM, the decision can be daunting. Both options have their unique advantages and challenges, and the best choice depends on your organization’s specific needs and goals.
Cloud CRM offers flexibility, scalability, and lower upfront costs, while On-Premise CRM provides more control, customization, and security. In this section, we will delve deeper into the key factors to consider when making this critical decision.
Cost Considerations
One of the most significant factors to consider is the cost. Cloud CRM typically involves a subscription-based model with lower upfront costs, making it more accessible for small to medium-sized businesses.
On the other hand, On-Premise CRM requires a substantial initial investment in hardware, software, and infrastructure, but may result in lower long-term costs if the system is well-maintained.
Additionally, Cloud CRM often includes ongoing support and updates, whereas On-Premise CRM may require additional expenses for maintenance and upgrades.
Security and Data Control
Data security and control are paramount for many organizations. Cloud CRM solutions are hosted by third-party providers, which can raise concerns about data privacy and compliance. However, reputable cloud providers often have robust security measures in place, including encryption, backups, and compliance certifications.
On-Premise CRM, on the other hand, gives organizations direct control over their data and infrastructure, allowing for more customized security protocols and compliance with industry regulations. This can be particularly important for businesses handling sensitive information.
Customization and Flexibility
The level of customization and flexibility is another critical factor. On-Premise CRM allows for extensive customization to meet specific business needs, including the integration of legacy systems and the creation of unique workflows.
Cloud CRM, while generally more standardized, has made significant strides in offering flexible configurations and integrations. However, the degree of customization is still generally more limited compared to On-Premise solutions. For businesses that require highly tailored systems, On-Premise CRM may be the better choice.
| Factor | Cloud CRM | On-Premise CRM |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Lower upfront costs, subscription-based model | Higher upfront costs, potential for lower long-term costs |
| Security | Robust security measures, third-party hosting | Direct control, customizable security protocols |
| Customization | Flexible configurations, limited customization | Extensive customization, integration with legacy systems |
Which is better, cloud or on-premise?
When deciding between cloud and on-premise solutions, several factors must be considered to determine which option is better suited for a specific organization.
Each approach has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, and the optimal choice often depends on the organization’s unique requirements, budget, and long-term strategic goals.
Cost Considerations
Cost is a significant factor when comparing cloud and on-premise solutions. Cloud services typically operate on a subscription model, where users pay a monthly or annual fee for access to the service. This model can be more predictable and scalable, allowing organizations to pay for only what they use.
On the other hand, on-premise solutions require an initial capital investment for hardware, software, and setup. Over time, on-premise solutions may incur additional costs for maintenance, upgrades, and personnel.
- Cloud services often have lower upfront costs, making them attractive for startups and small businesses with limited capital.
- On-premise solutions can become more cost-effective in the long run for large enterprises with significant IT infrastructure, as the per-unit cost of hardware and software can decrease with volume.
- Maintenance and support costs for on-premise solutions can be substantial, including ongoing expenses for updates and technical staff.
Data Security and Compliance
Data security and compliance are critical considerations for any organization. Cloud providers generally offer robust security measures, including data encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular security audits. However, the responsibility for securing data in the cloud is shared between the provider and the user.
On-premise solutions allow organizations to have full control over their data and security measures, which can be advantageous for industries with strict regulatory requirements.
- Cloud providers often have dedicated security teams and advanced security technologies that may be more comprehensive than what an organization can implement on its own.
- On-premise solutions can be tailored to meet specific compliance requirements, providing greater control over data governance and access.
- Data breaches in the cloud can have widespread implications, affecting multiple organizations, whereas on-premise breaches are typically more contained to the affected organization.
Scalability and Flexibility
Scalability and flexibility are key benefits of cloud solutions. Cloud services can easily scale up or down based on demand, allowing organizations to adapt quickly to changing business needs. This is particularly useful for businesses experiencing rapid growth or seasonal fluctuations.
On-premise solutions, while more rigid, can be customized to match an organization’s specific requirements and workflows.
- Cloud services provide seamless scalability, enabling organizations to add or remove resources as needed without significant downtime or additional hardware costs.
- On-premise solutions require more planning and lead time for scaling, as they often involve purchasing and configuring additional hardware and software.
- Customization is a strong point for on-premise solutions, allowing organizations to fine-tune their systems to optimize performance and meet unique business processes.
What is the difference between cloud CRM and on-premise CRM?
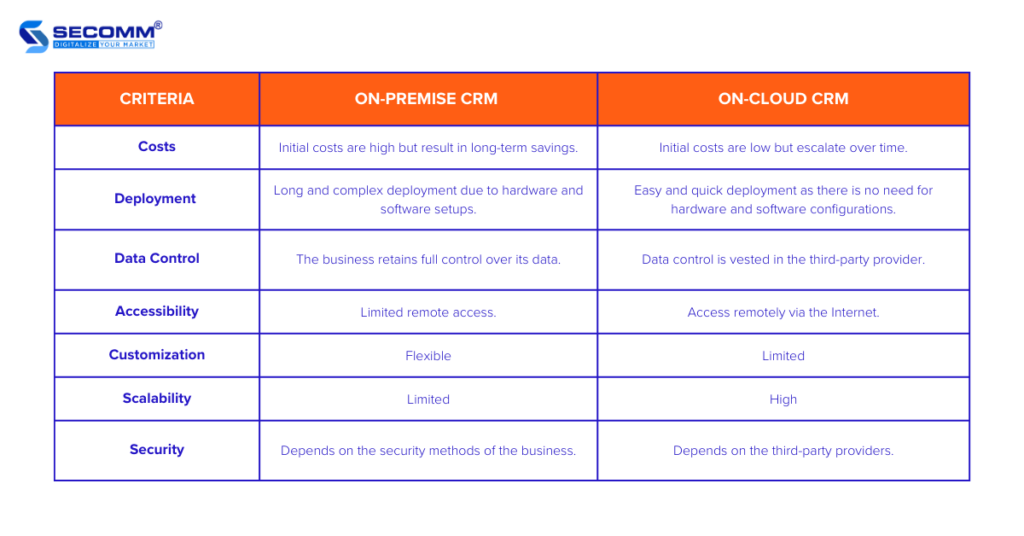
The primary difference between cloud CRM and on-premise CRM lies in how the software is hosted, managed, and accessed. Cloud CRM, also known as Software as a Service (SaaS), is hosted on external servers provided by a third-party vendor.
Users access the CRM system via the internet, typically through a web browser. On the other hand, on-premise CRM is installed and hosted on the company’s own servers, requiring a dedicated IT infrastructure for management and maintenance.
Cost Structure and Scalability
In terms of cost structure, cloud CRM generally operates on a subscription-based model, where users pay a recurring fee based on the number of users or the features they need. This model allows for greater scalability, as businesses can easily add or remove users and features as needed without incurring significant upfront costs.
In contrast, on-premise CRM often requires a substantial initial investment for hardware, software, and installation. Ongoing costs include maintenance, updates, and IT personnel to manage the system.
- Cloud CRM: Subscription fees, predictable costs, easy to scale.
- On-premise CRM: High initial costs, variable ongoing expenses, more control over resources.
- Cloud CRM: No need for additional hardware, on-premise CRM requires dedicated servers.
Data Security and Compliance
Data security and compliance are critical considerations for any CRM system. Cloud CRM providers typically implement robust security measures, including data encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular backups. However, because the data is stored off-site, some organizations may have concerns about data sovereignty and compliance with local regulations.
On-premise CRM, while offering more control over data and potentially better compliance with specific regulations, may require more effort and resources to maintain high levels of security.
- Cloud CRM: Centralized security measures, regular updates, and compliance with industry standards.
- On-premise CRM: Greater control over data and security practices, potentially better for specific regulatory requirements.
- Cloud CRM: May have limitations in data location and sovereignty, on-premise CRM ensures data remains within the organization’s premises.
Customization and Integration
Customization and integration capabilities are important factors for businesses looking to tailor their CRM system to their specific needs. Cloud CRM solutions often offer a range of pre-built integrations with other business tools and platforms, and while they may have some limitations in terms of custom development, many providers offer app marketplaces and APIs to extend functionality.
On-premise CRM systems, with their more flexible architecture, can be extensively customized and integrated with existing systems and processes, but this often requires specialized IT skills and can be time-consuming.
- Cloud CRM: Pre-built integrations, app marketplaces, and APIs for flexibility.
- On-premise CRM: Highly customizable and integrable, but requires significant IT resources.
- Cloud CRM: Faster deployment and updates, on-premise CRM allows for deeper integration with legacy systems.
What are the benefits of Dynamics 365 cloud vs on-premise?
When deciding between Dynamics 365 cloud and on-premise solutions, several factors come into play. Here are the key benefits of choosing the cloud version:
Cost Efficiency and Scalability
One of the primary advantages of Dynamics 365 cloud is cost efficiency and scalability. The cloud model operates on a subscription-based pricing structure, which means you pay only for what you use. This can significantly reduce upfront capital expenditures and ongoing maintenance costs.
Moreover, the cloud solution allows for easy scaling of resources as your business grows or contracts. You can add or remove users, storage, and computing power without the need for additional hardware or complex configurations.
- Reduced initial investment in hardware and infrastructure
- Flexibility to scale resources up or down based on business needs
- Avoidance of large capital expenditures and predictable monthly costs
Accessibility and Mobility
Dynamics 365 cloud offers unparalleled accessibility and mobility. With a cloud-based solution, your data and applications are accessible from any device with an internet connection, making it easy for employees to work from anywhere. This is particularly beneficial for businesses with remote workers or a distributed workforce.
The mobility provided by the cloud enhances collaboration and productivity, as employees can stay connected and work seamlessly, regardless of their location.
- Accessibility from any device with an internet connection
- Enhanced collaboration and productivity for remote workers
- Real-time data access and updates for informed decision-making
Maintenance and Upgrades
Maintaining and upgrading an on-premise solution can be a time-consuming and resource-intensive process. With Dynamics 365 cloud, Microsoft handles the maintenance, security, and software updates, freeing up your IT staff to focus on more strategic initiatives.
This ensures that you always have access to the latest features and security patches without the need for manual intervention.
- Automatic software updates and security patches
- Reduced burden on IT staff for maintenance and support
- Access to the latest features and improvements without downtime
What are the 4 types of CRM?
The four main types of Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems are Operational CRM, Analytical CRM, Collaborative CRM, and Strategic CRM. Each type serves distinct purposes in managing customer interactions, analyzing data, and fostering better business relationships.
Operational CRM
Operational CRM focuses on streamlining and automating business processes to improve the efficiency of customer interactions. This type of CRM system handles the core processes of sales, marketing, and customer service. By automating these processes, Operational CRM helps businesses reduce manual efforts and enhance productivity.
– Sales: Automates sales processes such as lead management, opportunity tracking, and sales forecasting.
– Marketing: Manages marketing campaigns, lead generation, and customer segmentation.
– Customer Service: Facilitates support services, case management, and service request tracking.
Analytical CRM
Analytical CRM is designed to analyze customer data to gain insights and drive business decisions. This type of CRM system uses data mining, statistical analysis, and reporting tools to provide a deeper understanding of customer behavior and preferences.
By leveraging these insights, businesses can tailor their strategies to better meet customer needs and improve overall performance.
– Data Collection: Gathers data from various sources including sales, marketing, and customer service.
– Data Analysis: Uses advanced analytics to identify trends, patterns, and customer behaviors.
– Reporting: Generates reports and dashboards to visualize key metrics and insights.
Collaborative CRM
Collaborative CRM, also known as Customer Interaction Management (CIM), focuses on improving communication and collaboration among different departments within a business and between the business and its customers.
This type of CRM system facilitates the sharing of customer information and insights across various channels, ensuring a unified and consistent customer experience.
– Customer Interaction: Manages interactions across multiple channels such as email, phone, chat, and social media.
– Information Sharing: Enables seamless sharing of customer data between departments.
– Cross-Department Collaboration: Fosters collaboration and coordination among sales, marketing, and service teams.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main differences between Cloud and On-Premise CRM solutions?
The primary differences lie in deployment and management. Cloud CRM is hosted online, accessible via the internet, and typically managed by the provider. On-Premise CRM is installed on local servers, offering greater control over data and security but requiring more maintenance and IT resources.
What are the cost implications of choosing Cloud vs. On-Premise CRM?
Cloud CRM often operates on a subscription model with predictable, ongoing costs and minimal upfront fees. On-Premise CRM can involve significant initial expenses for hardware and software but may have lower long-term operational costs, depending on the organization’s size and IT capabilities.
How do Cloud and On-Premise CRM systems differ in terms of security?
Cloud CRM providers typically implement robust security measures, including data encryption and regular backups. On-Premise CRM allows for customized security protocols and physical control over data, which can be crucial for highly sensitive information, but it also requires constant oversight and updates.
What are the scalability options for Cloud and On-Premise CRM?
Cloud CRM is highly scalable, allowing for easy adjustments to storage and user capacity as business needs change. On-Premise CRM requires additional hardware and software investments for scaling, which can be more complex and time-consuming to implement.